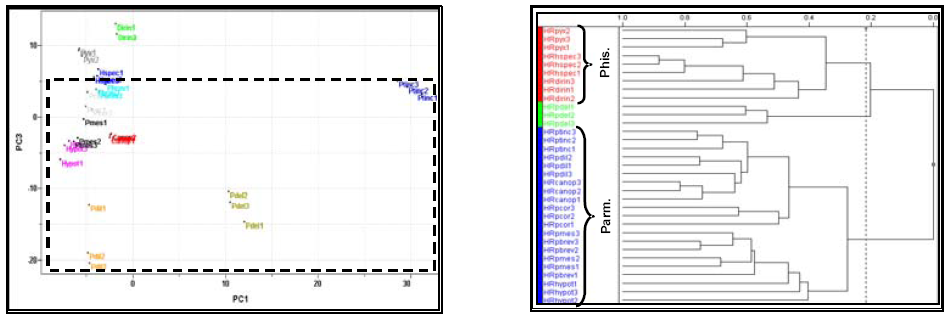
Figure 1: HCA plot of all lichens in HR-MAS NMRFigure 2: PCA scores plot of all lichens in IR
analysis (similarity 0.217).analysis. (PC1xPC3, 21,9 and 14.6%).
Alcântara G. B., Honda N. K., Ferreira M. M. C., Ferreira A. G., "Chemometric analysis applied in intact lichens samples using (HR-MAS) 1H NMR and IR data for chemotaxonomic discrimination". Águas de Lindóia, SP, Brazil, 10-15/09/2006: 10th International Conference on Chemometrics in Analytical Chemistry (CAC-2006, CAC-X), Book of Abstracts (2006) P019. Poster 019.
10th International Conference on Chemometrics in Analytical Chemistry P019
Chemometric analysis applied
in intact lichens samples using
(HR-MAS) 1H
NMR and IR data for chemotaxonomic
discrimination
Glaucia Braz Alcantara1*,
Neli Kika Konda2, Márcia Miguel
Castro Ferreira3,
Antonio
Gilberto Ferreira1
glabraz@yahoo.com.br
1 Departamento
de Química, Universidade Federal de São Carlos, São
Carlos/SP - Brazil.
2 Departamento
de Química, Universidade Federal de Mato Grosso do Sul, Campo Grande/MS
- Brazil.
2 Instituto de
Química, Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Campinas/SP - Brazil.
Keywords: lichen, NMR,
IR
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Lichens present a difficult morphologial differentiation
and usually the chemical analyses are
very
employed for
its taxonomic classification, mainly due
to the secondary metabolites to be
relatively
constant for
these organisms1. The
chemotaxonomic lichens classification usually is realises
by colour
reactions, chromatography,
fluorescence and mass spectrometry
analysis2. However, this
majority
analysis involves
pre-treatment sample process with a high time
and reagents consumption. Therefore,
fast analysis methods
that dispense the smaples manipulation are very
required, being able to present
great importance for lichens
chemotaxonomy.
In this work we focus the application of HR-MAS 1H
NMR (High Resolution Magic Angle Spinning) and
IR, both techniques
using intact samples associated with chemometric analysis.
For this purpose, eleven
species of lichens sample
from six genera and two different families were
powdered in a cryogenic mill.
1H HR-MAD NMR
spectra were obtained on a Bruker 9.4 Tesla DRX 400 Bruker
spectrometer, equipped
with a 4 mm
HR-MAS probehead and zirconia rotor. IR spectra were registered in
a Bomem Hartmann &
Braun MB-Series
model 102 spectrometer. All spectra were
used as input variabvle on the Pirouette®
software to perform chemometric
analysis by PCA and HCA methods.
Chemometric analysis of HR-MAS 1H
NMR and IR spectra has permitted to correlate
the families,
genera and species.
In Figure 1, we can observe
the discrimination between Phisciaceae
and
Parmeliaceae families in
the HR-MAS 1H NMR data with only one sample
presenting an unusual behaviour.
In Figure 2,
the PCA scores plot show families discrimination
using IR data (Parmeliaceae family is
presented in hatched square).
In comparison with other traditional techniques,
HR-MAS 1H NMR and IR
allied with chemometrics
have provided a
fast and economic method for lichens chemotaxonomy.
Both methods were useful for
lichens analysis and
have permitted the satisfactory discrimination between families,
genera and species.

Figure
1: HCA plot
of all lichens in HR-MAS NMRFigure
2: PCA scores plot of all lichens
in IR
analysis
(similarity 0.217).analysis.
(PC1xPC3, 21,9 and 14.6%).
Acknowledgment
- Fapesp, CNPq, Capes, Finep.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
References
1 Quilhot W.;
Leighton G.; Flores E.; Fernandes E.; Pena W.; Guzman G. Acta Farm.
Boranense, 1987,
6(1): 15-22.
2 Honda N. K.;
Vilegas W. Quím. Nova, 1998, 21(6): 110-125.