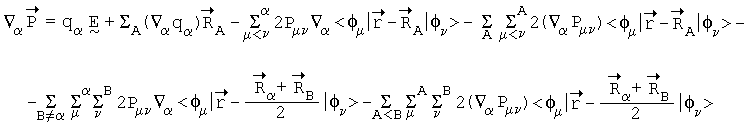
Ferreira M. M. C., "Partição de Tensores Polares Atômicos" ["Partition of Atomic Polar Tensors"]. Fortaleza, CE, 09-15/07/1989: 41a Reunião Anual da Sociedade Brasileira para o Progresso da Ciência [The 41st Annual Meeting of the Brasilian Society for the Progress of Science], Cienc. Cult., 41(Suppl) (1989) 597. Poster 25-D.2.10.
25-D.2.10 PARTIÇÃO DE TENSORES POLARES ATÔMICOS. Márcia Miguel Castro Ferreira (Depto de Físico-Química, I.Q.-Universidade Estadual de Campinas).
Obtendo-se o gradiente da expressão
usada para o cálculo do momento dipolar, invariante à origem
do sistema de coordenadas, chega-se a uma expressão geral para o
cálculo do Tensor Polar Atômico (TPA), quantidade está
diretamente ligada às Intensidades Infravermelhas de moléculas
na fase gasosa. Daí, a importância de se tentar interpretar
o TPA através de um modelo de partição.
A expressão geral obtida para
o Tensor Polar do átomo a
é:
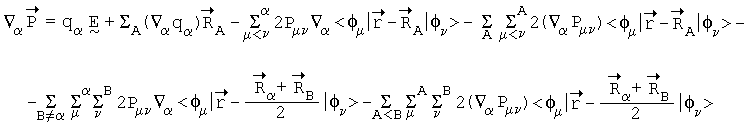
onde
![]()
é a matriz identidade. As duas
primeiras contribuições são já bem conhecidas
e se referem à "carga" e "fluxo de carga". As duas seguintes são
ligadas às hibridizações nos diversos átomos
e as duas últimas são contribuições de ligação.
Cálculos feitos para moléculas de H2O e NH2
indicam que o TPA para o átomo de hidrogênio têm basicamente
características atômicas e uma tendência da molécula
a se dissociar em átomos.
25-D.2.10 PARTITION OF ATOMIC POLAR TENSORS. Márcia Miguel Castro Ferreira (Depto de Físico-Química, I.Q.-Universidade Estadual de Campinas).
After obtaining the expression for the dipole moment calculation, which is invariant to coordinate systems, the expression for calculation of Atomic Polar Tensor (APT), a quantity that is directly related to the infrared intensities of gas-phase molecules, is generalized. This is the reason for TPA interpretation in terms of a partition model. The general expression for the Polar Tensor of the atom a is:
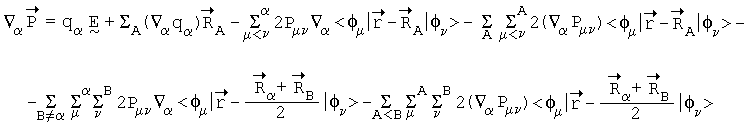
where
![]()
is the identity matrix. The first
two contributions are well-known and are related to "charge" and "charge
flux". The other two contributions are related to hybridizations of different
atoms, and the last two are contributions of chemical bonding. The calculations
performed for molecules H2O and NH2 indicate that
the APT for hydrogen atom has mainly the atomic characteristics and the
molecule tends to dissociate into its atoms.